資料結構大致上可以分為 linear 和 non-linear 兩種類別,其中 linear data structure 包含 array, linked-list stack, queue, non-linear data structure 包含 trees, graphs。
其中 non-linear 其實也可以用 linear data structure 來表示,因此先來介紹 linear data structure。
Table of Contents
1. Linear data structure 定義
- 元素之間有順序性的
- 若元素存在多個,則第一個元素沒有 predecessor (前驅元素),最後一個元素沒有 successor (後繼元素)
- 除了第一個元素和最後一個元素,其餘元素都只有一個 predecessor 和 successor
Linear data structure 按照儲存方式又分為:
- Sequential list (循序儲存結構):Array
- Linked list (鏈式儲存結構):Linked-list
有些文章會把 stack 和 queue 歸類在循序儲存結構,但實際上 stack 和 queue 也都存在鏈式儲存結構。
2. Array (陣列)
Array 為 linear data structure 的循序儲存結構,指的是會分配一段連續記憶體位置來儲存這個 linear list。因此一般來說在高階的程式語言中 array 的長度是固定的,除了 JavaScript 之外!JavaScript 的 array 長度是可以隨著元素的增減自動伸縮。但舉例來說,在 go 裡面,array 一旦宣告了,長度就是固定的,若是要使用像 JavaScript 中 array 的 data structure,則必需用 slice 這個資料型態。
2.1 時間複雜度
對 array CRUD 的 time complexity (Average)
| Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion |
| O(1) | O(n) | O(n) | O(n) |
3. Linked-list (鏈結串列)
Linked-list 為 linear data structure 的鏈式儲存結構。在 array 中,宣告時即確定了該 array 的長度,因此如果宣告的長度太小,則需要重新宣告新的 array,宣告的長度太大,則會造成記憶體空間的浪費。
Linked-list 和 array 最大的差別則是記憶體儲存的位置是不連續的。Linked-list 的每個元素稱為 node (節點),每個 node 由 data 和 pointer (指標) 組成,其中又分為以下三種:
3.1 分類
3.1.1 Singly Linked-list
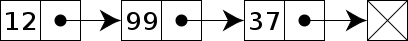
每個 node 的 pointer 會指向下一個 node。
3.1.2 Doubly Linked-list

每個 node 有兩個 pointer,一個指向前面的 node,另一個指向後面的 node。
3.1.3 Circular Linked-list
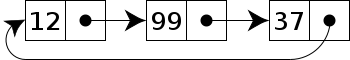
和 singly linked-list 一樣,每個 node 都只有一個 pointer,唯一的差別是最後一個 node 的 pointer 會指向第一個 node。
3.2 JavaScript 實作
3.2.1 node
class Node {
constructor(data, next = null) {
this.data = data;
this.next = next;
}
}3.2.2 Singly linked-list
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
}
insertFirst(data) {
this.insertAt(data, 0);
}
size() {
let counter = 0;
let node = this.head;
while (node) {
counter++;
node = node.next;
}
return counter;
}
getFirst() {
return this.getAt(0);
}
getLast() {
return this.getAt(this.size() - 1);
}
clear() {
this.head = null;
}
removeFirst() {
if (!this.head) {
return;
}
this.head = this.head.next;
}
removeLast() {
if (!this.head) {
return;
}
if (!this.head.next) {
this.head = null;
return;
}
let previous = this.head;
let node = this.head.next;
while (node.next) {
previous = node;
node = node.next;
}
previous.next = null;
}
insertLast(data) {
const lastNode = this.getLast();
if (lastNode) {
lastNode.next = new Node(data);
} else {
this.head = new Node(data);
}
}
getAt(index) {
let counter = 0;
let node = this.head;
while (node) {
if (counter === index) {
return node;
}
counter++;
node = node.next;
}
return null;
}
removeAt(index) {
if (!this.head) {
return;
}
if (index === 0) {
this.head = this.head.next;
return;
}
if (index > this.size()) {
return;
}
const previous = this.getAt(index - 1);
if (!previous || !previous.next) {
return;
}
previous.next = previous.next.next;
}
insertAt(data, index) {
if (!this.head) {
this.head = new Node(data);
return;
}
if (index === 0) {
this.head = new Node(data, this.head);
return;
}
const previous = this.getAt(index - 1) || this.getLast();
const node = new Node(data, previous.next);
previous.next = node;
}
forEach(fn) {
let node = this.head;
let counter = 0;
while (node) {
fn(node, counter);
node = node.next;
counter++;
}
}
*[Symbol.iterator]() {
let node = this.head;
while (node) {
yield node;
node = node.next;
}
}
}3.3 時間複雜度
對 linked-list CRUD 的 time complexity (Average)
| Access | Search | Insertion | Deletion |
| O(n) | O(n) | O(1) | O(1) |
4. Linked-list, Array 比較
| Array | Linked-list | |
| 優點 | • 可以用 index 快速存取元素 (O(1)) • 較節省記憶體空間,因為 linked-list 需要額外分配記憶體給 pointer | • 長度不固定,不用預先分配記憶體給 linked-list • insert 和 delete 的時間複雜度為 O(1) |
| 缺點 | • 長度不可改變,宣告太長浪費記憶體空間,宣告太短則不夠用 • insert 和 delete 的時間複雜度為 O(n) | • 存取元素的時間複雜度為 O(n) • 記憶體使用量較 array 大 |
5. 參考資料
大話資料結構(全新彩色版)
JavaScript 學演算法
Difference between Linear and Non-linear Data Structures
Big-O Cheat Sheet
資結與演算法筆記 (1)— linked list 與 array 於O(n)之差異比較
The Coding Interview Bootcamp: Algorithms + Data Structures
如果覺得我的文章有幫助的話,歡迎幫我的粉專按讚哦~謝謝你!

